Direct Taxation
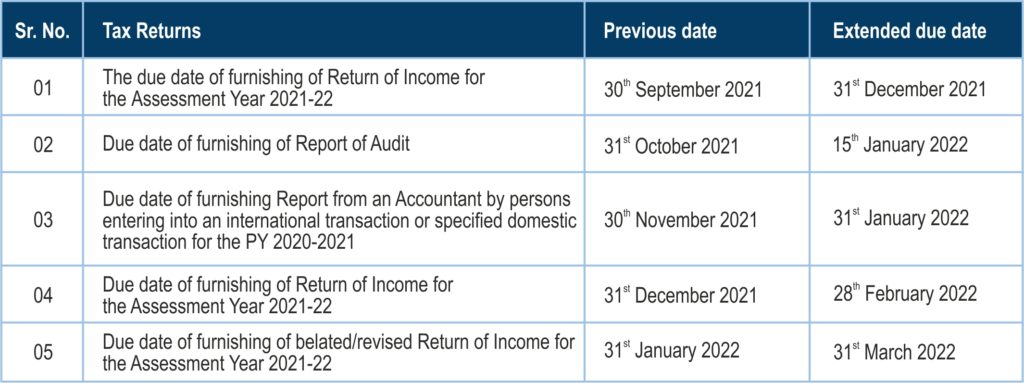
CBDT extends due dates for filing Income tax returns and various reports of Audit for Assessment year 2021-22
The Ministry of Finance on 9th September 2021 has extended the due dates for filing of Income Tax Returns and various reports of audit for the Assessment Year 2021-22 on considering the difficulties reported by the taxpayers and other stakeholders in the filing of Income Tax Returns.
The revised due date is as follows:
Further, in the case of an individual resident in India referred to in sub-section (2) of section 207 of the Act, the tax paid by him under section 140A of the Act within the due date, provided in that Act, shall be deemed to be the advance tax.
Income Tax (25th Amendment) Rules, 2021
The Central Board of Direct Taxes through circular dated 31st August 2021 has issued the Income-tax (25th Amendment) Rules, 2021. The amendment provides that while calculating taxable interest relating to contribution in a provident fund or recognized provided fund, exceeding the specified limit, non-taxable contribution account shall be the aggregate of the following, namely: –
- Closing balance in the account as on 31st day of March 2021.
- Any contribution made by the person in the account during the previous year 2021-2022 and Subsequent previous years, which is not included in the taxable contribution account; etc.
These rules will come into force on the 1st day of April 2022.
CBDT clarification regarding carry forward of losses in case of change in shareholding due to strategic disinvestment
CBDT through a press release dated 10 September 2021 has issued clarification regarding carry forward of losses in case of change in shareholding due to strategic disinvestment. Previously, any loss incurred in any previous year prior to, and including, the previous year of strategic disinvestment shall be carried forward and set off by the erstwhile public sector company.
The above relaxation shall cease to apply from the previous year in which the company, that was the ultimate holding company of such erstwhile public sector company immediately after completion of the strategic disinvestment, ceases to hold, directly or through its subsidiary or subsidiaries, fifty-one per cent of the voting power of the erstwhile public sector company. Necessary legislative amendments for the above decision shall be proposed in due course of time.
Central Government relaxes provisions of TDS u/s 194A of the Income-tax Act, 1961 in view of section of 10(26) of the Act
The Central Government in the exercise of the powers conferred by sub-section (1F) of section 197A of the Income-tax Act, 1961 (“the Act”) has notified that no deduction of tax shall be made on the following payment under section 194A of the Act, namely payment in the nature of interest, other than interest on securities, made by a Scheduled Bank (hereinafter the ‘payer’) located in a specified area to a member of Scheduled Tribe (hereinafter the ‘receiver’) residing in any specified area as referred to in S. 10(26) of the Act, subject to the following conditions:
i) the payer satisfies itself that the receiver is a member of Scheduled Tribe residing in any specified area, and the payment as referred above is accruing or arising to the receiver as referred to in section 10(26) of the Act, during the previous year relevant for the assessment year in which the payment is made, by obtaining necessary documentary evidence in support of the same.
ii) the payer reports the above payment in the statements of deduction of tax as referred to in sub-section (3) of section 200 of the Act.
iii) the payment made or aggregate of payments made during the previous year does not exceed twenty lakh rupees.
For the purposes of the said notification, ‘Scheduled Bank’ means a bank included in the Second Schedule of the Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934.
CBDT notifies Safe Harbour Rules retrospectively applicable for AY 2021-22
The CBDT notifies Safe Harbour Rules will be applied retroactively for Assessment Year 2021-22.
The Board of Revenue has published the Income-tax (30th Amendment) Rules, 2021, which revise the Income-tax Rules, 1962.
The words and figures “the assessment year 2020-21” shall be substituted for the words and figures “assessment years 2020-21 and 2021-22” in rule 10TD, sub-rule (3B), of the Income-tax Rules, 1962.
The Safe Harbour Rules and process are covered by Rule 10TD of the Income Tax Rules, 1962. Changes to these laws were announced by the CBDT, who said that rates in effect from Assessment Year 2017-18 to 2020-21 will continue to be in effect for Assessment Year 2021-22.
If an eligible assessee enters into an eligible international transaction and the option exercised by the said assessee is not held to be invalid under rule 10TE, the transfer price declared by the assessee in respect of such transaction shall be accepted by the income-tax authorities if it is in accordance with the circumstances specified in sub-rule (2) or (2A). Only Rule 2A was applicable from Assessment Year 2017-18 to Assessment Year 2020-21, but this was recently extended to Assessment Year 2021-22 as well.
They will be considered in effect as of April 1, 2021.
Indirect Taxation
Key Recommendation of 45th GST Council meeting
The GST Council’s 45th meeting was held on 17th September 2021 under the chairmanship of the Union Finance & Corporate Affairs Minister Smt. Nirmala Sitharaman. The GST Council has inter-alia made the following recommendations relating to changes in GST rates on supply of goods and services and changes related to GST law and procedure:
COVID- 19 relief measures have been extended till December 31, 2021. There is a reduction of GST rate to 5 per cent on some more Covid-19 treatment drugs till December 31 and there have been changes in rates on a range of goods.
GST rate on Keytruda medicine for the treatment of cancer reduced from 12% to 5%. GST rates on Retro fitment kits for vehicles used by persons with special abilities were reduced to 5%. GST rates on Fortified Rice kernels for schemes like ICDS reduced from 18% to 5%.
Brick kilns have been brought under a special composition scheme with a threshold limit of Rs 20 lakh.
Validity of GST exemption on the transport of goods by vessel and air from India to outside India is extended up to 30.9.2022.
Requirement of filing FORM GST ITC-04 under rule 45 (3) of the CGST Rules has been relaxed as under:
- Taxpayers whose annual aggregate turnover in preceding financial year is above Rs. 5 crores shall furnish ITC-04 once in six months.
- Taxpayers whose annual aggregate turnover in preceding financial year is upto Rs. 5 crores shall furnish ITC-04 annually.
GST on specified Renewable Energy Projects can be paid in terms of the 70:30 ratio for goods and services, respectively, during the period from 1.7.2017 to 31.12.2018, in the same manner as has been prescribed for the period on or after 1st January 2019.
Essentiality certificate issued by Directorate General of Hydrocarbons on imports would suffice; no need for taking a certificate every time on inter-state stock transfer.
All laboratory reagents and other goods falling under heading 3822 attract GST at the rate of 12%
External batteries sold along with UPS Systems/ Inverter attract GST rate applicable to batteries [28% for batteries other than lithium-ion battery] while UPS/inverter would attract 18%.
E-Commerce Operators are being made liable to pay tax on the following services provided through them:
- Transport of passengers, by any type of motor vehicles through it [w.e.f. 1st January 2022]
- Restaurant services provided through it with some exceptions [w.e.f. 1st January 2022
Alcoholic liquor for human consumption is not food and food products for the purpose of the entry prescribing 5% GST rate on job work services in relation to food and food products.
Services by cloud kitchens/central kitchens are covered under ‘restaurant service’ and attract 5% GST.
Various notifications all dated 30th September 2021, have been issued under GST laws and Custom Laws to carry out changes in rates and exemption of various goods and services as recommended by GST council in its 45th Meeting held on 17th September 2021. Detailed analysis of all notifications will be covered in supplementary article.
CBIC issues clarification relating to Export of Services-condition (v) of section 2(6) of the IGST Act 2017.
The Central Board of Indirect Taxes and Customs on 20th September 2021 has issued a clarification on the conditions of export of services. The terms export service is defined under section 2(6) of IGST Act, which means the supply of any service when the supplier of service and the recipient of service are not merely establishments of a distinct person in accordance with Explanation 1 in section 8.
Various representations have been received citing ambiguity caused in the interpretation of Explanation 1 under section 8 of the IGST Act 2017 in relation to condition (v) of export of services. Doubts have been raised whether the supply of service by a subsidiary/ sister concern/ group concern, etc. of a foreign company in India, which is incorporated under the laws in India, to the foreign company incorporated under laws of a country outside India, will hit by condition (v) of subsection (6) of section 2 of IGST Act.
Explanation 1 of Section 8 of the IGST Act provides for the conditions wherein establishments of a person would be treated as establishments of distinct persons.
Through this notification, CBDT has clarified that a company incorporated in India and a body corporate incorporated by or under the laws of a country outside India, which is also referred to as a foreign company under the Companies Act, are separate persons under CGST Act, and thus are separate legal entities. Accordingly, these two separate persons would not be considered as “merely establishments of a distinct person in accordance with Explanation 1 in section 8”.
Therefore, supply of services by a subsidiary/ sister concern/ group concern, etc. of a foreign company, which is incorporated in India under the Companies Act, 2013, to the establishments of the said foreign company located outside India (incorporated outside India), would not be barred by the condition (v) of the sub-section (6) of section 2 of the IGST Act 2017 for being considered as export of services, as it would not be treated as supply between mere establishments of distinct persons under Explanation 1 of section 8 of IGST Act 2017.
Similarly, the supply from a company incorporated in India to its related establishments outside India, which are incorporated under the laws outside India, would not be treated as supply to merely establishments of a distinct person under Explanation 1 of section 8 of IGST Act 2017. Such supplies, therefore, would qualify as ‘export of services, subject to fulfilment of other conditions as provided under sub-section (6) of section 2 of the IGST Act.
CBIC issues clarification on doubt related to the scope of intermediary.
The Central Board of Indirect Taxes and Customs on 20th September 2021 has issued Clarification on doubts related to the scope of “Intermediary. The term Intermediary has been defined under section 2(13) of the Integrated Goods and Services Tax Act, 2017 which means a broker, an agent, or any other person, by whatever name called, who arranges or facilitates the supply of goods or services or both, or securities, between two or more persons, but does not include a person who supplies such goods or services or both or securities on his own account.
The concept of intermediary services, as defined above, requires some basic prerequisites, which are a minimum of three parties, two distinct supplies, Intermediary service provider to have the character of an agent, broker or any other similar person and does not include a person who supplies such goods or services or both or securities on his own account.
An important exclusion from an intermediary is sub-contracting. The supplier of the main service may decide to outsource the supply of the main service, either fully or partly, to one or more subcontractors. Such sub-contractor provides the main supply, either fully or a part thereof, and does not merely arrange or facilitate the main supply between the principal supplier and his customers, and therefore, clearly is not an intermediary.
The specific provision of a place of supply of ‘intermediary services’ under section 13 of the IGST Act shall be invoked only when either the location of supplier of intermediary services or location of the recipient of intermediary services is outside India.
Clarification In Respect of Section 16(4) For Debit Notes, Carrying Physical Copy Of E-Invoice During Transportation & Refund of GST On Goods Where Export Duty Is Applicable
- SECTION 16(4) FOR DEBIT NOTES:
From 1.1.2021, where for Debit Notes ITC can be availed by 30th September of the next FY by the counterparty. Which of the following dates are relevant to determine the ‘financial year’ for the purpose of section 16(4):
(a) date of issuance of the debit note, or
(b) date of issuance of underlying invoice.
Answer: w.e.f. 01.01.2021, in the case of debit notes, the date of issuance of debit notes (not the date of underlying invoice) shall determine the relevant financial year for the purpose of section 16(4) of the CGST Act.
Whether any availment of the input tax credit, on or after 01.01.2021, in respect of debit notes issued either prior to or after 01.01.2021, will be governed by the provisions of the amended section 16(4), or the amended provision will be applicable only in respect of the debit notes issued after 01.01.2021?
Answer: The availment of ITC on debit notes in respect of amended provision shall be applicable from 01.01.2021. Accordingly, for availment of ITC on or after 01.01.2021, one has to only see the date of issue of the debit note.
For Debit Note issued after 01.01.2021, the eligibility for availment of ITC will be governed by the amended provision of section 16(4). For the Debit note issued prior to 01.01.2021, the provisions of section 16(4), as it existed before the said amendment on 01.01.2021.
- CARRYING PHYSICAL COPY OF E-INVOICE DURING TRANSPORTATION:
Whether carrying a physical copy of an invoice is compulsory during movement of goods in cases where suppliers have issued invoices in the manner prescribed under rule 48 (4) of the CGST Rules, 2017 (i.e. in cases of e-invoice)
Answer: There is no need to carry the physical copy of tax invoice in cases where an e-invoice has been generated by the supplier in the manner prescribed under rule 48(4) of the CGST Rules and production of the Quick Response (QR) code having an embedded Invoice Reference Number (IRN) electronically, for verification by the proper officer.
- REFUND OF GST ON GOODS WHERE EXPORT DUTY IS APPLICABLE:
Whether the first proviso to section 54(3) of CGST / SGST Act, prohibiting refund of unutilized ITC is applicable in case of exports of goods which are having NIL rate of export duty.
Answer: Only those goods which are actually subjected to export duty i.e., on which some export duty has to be paid at the time of export, will be covered under the restriction imposed under section 54(3) from availment of refund of accumulated ITC. Goods, which are not subject to any export duty and in respect of which either NIL rate is specified in Second Schedule to the Customs Tariff Act, 1975 or which are fully exempted from payment of export duty by virtue of any customs notification or which are not covered under Second Schedule to the Customs Tariff Act, 1975, would not be covered by the restriction imposed under the first proviso to section 54(3) of the CGST Act for the purpose of availment of refund of accumulated ITC.
Foreign Trade Policy
The government from time to time have been extending the applicability & validity of Foreign Trade Policy (FTP). The last such extension was made up to 30th September 2021. The government further extended the validity of FTP up to 31st March 2022. Notification No 33 dated 28th September,21 in this regards are issued which is attached for reference.
Ministry of Commerce notifies the last date for submitting applications for scrip-based FTP schemes and validity period of duty credit scrips.
The Ministry of Commerce and Industry on 16th September 2021 has extended the last date for submitting online applications for Script-based FTP Schemes till 31st December 2021.
The last date for submitting online applications stands revised to 31st December 2021 for the following schemes:
- MEIS (for exports made in the period (s) 01.07.2018 to 31.03.2019, 01.04.2019 to 31.03.2020 and 01.04.2020 to 31.12.2020)
- SEIS (for service exports rendered in FY 18-19 and FY 2019-20).
- 2% additional ad hoc incentive (under para 3.25 of the FTP-for exports made in the period 01.01.2020 to 31.03.2020 only),
- ROSCTL (for exports made from 07.03.2019 to 31.12.2020),
- ROSL (for exports made upto 06.03.2019 for which claims have not yet been disbursed under scrip mechanism).
- After 31.12.2021, no further applications would be allowed to be submitted and they would become time-barred. Late cut provisions shall also not be available for submitting claims at a later date.
Further, the validity of any scrip issued under FTP from the date of this Notification has been notified to be 12 months from the date of issue, in supersession of validity provisions in the Handbook of Procedures, 2015-20.
Ministry of Corporate Affairs (MCA)
MCA relaxes the last date of filing of cost audit report to the board of directors
The circular states that if a cost-audit report for the financial year 2020-21 by the cost auditor to the Board of Directors of the companies is submitted by October 31, 2021, then the same would not be viewed as a violation of rule 6(5) of Companies (cost records and audit) Rules, 2014. Therefore, the cost audit report for the financial year ended on March 31, 2021, shall be filed in e-form CRA-4 within 30 days from the date of receipt of the copy of the cost audit report by the company. However, in case a company has got an extension of time for holding Annual General Meeting under section 96(1) of the Act then e-form CRA-4 may be filed within the timeline provided under the proviso to rule 6(6) of the Companies (Cost Records and Audit) Rules, 2014.
SEBI
SEBI mandates certification requirement for principal officer/employees of Portfolio Managers
1. The associated persons functioning as the principal officer of a Portfolio Manager or employee(s) of the Portfolio Manager having decision making authority related to funding management, shall obtain certification from the National Institute of Securities Markets bypassing the NISM-Series-XXI-B: Portfolio Managers Certification Examination as mentioned in the communiqué No. NISM/Certification/Series-XXI-B: Portfolio Managers (PM) Certification/2021/01 dated June 15, 2021, issued by the National Institute of Securities Markets.
2. The Portfolio Managers shall ensure that all such associated persons who are principal officers or employees having decision making authority related to funding management as on the date of this notification obtain the certification by passing the NISM-Series-XXI-B: Portfolio Managers Certification Examination within two years from the date of this notification:
Provided that a Portfolio Manager, who engages or employs any such associated person who is a principal officer or an employee having decision making authority related to funding management, after the date of this notification, shall ensure that such person obtains certification by passing the NISM-Series-XXI-B: Portfolio Managers Certification Examination within one year from the date of their employment.